Portal:Mathematics
The Mathematics Portal
Mathematics is the study of representing and reasoning about abstract objects (such as numbers, points, spaces, sets, structures, and games). Mathematics is used throughout the world as an essential tool in many fields, including natural science, engineering, medicine, and the social sciences. Applied mathematics, the branch of mathematics concerned with application of mathematical knowledge to other fields, inspires and makes use of new mathematical discoveries and sometimes leads to the development of entirely new mathematical disciplines, such as statistics and game theory. Mathematicians also engage in pure mathematics, or mathematics for its own sake, without having any application in mind. There is no clear line separating pure and applied mathematics, and practical applications for what began as pure mathematics are often discovered. (Full article...)
Featured articles –
Selected image –

Good articles –
Did you know (auto-generated) –

- ... that more than 60 scientific papers authored by mathematician Paul Erdős were published posthumously?
- ... that in 1940 Xu Ruiyun became the first Chinese woman to receive a PhD in mathematics?
- ... that The Math Myth advocates for American high schools to stop requiring advanced algebra?
- ... that multiple mathematics competitions have made use of Sophie Germain's identity?
- ... that in the aftermath of the American Civil War, the only Black-led organization providing teachers to formerly enslaved people was the African Civilization Society?
- ... that despite a mathematical model deeming the ice cream bar flavour Goody Goody Gum Drops impossible, it was still created?
- ... that after Archimedes first defined convex curves, mathematicians lost interest in their analysis until the 19th century, more than two millennia later?
- ... that the British National Hospital Service Reserve trained volunteers to carry out first aid in the aftermath of a nuclear or chemical attack?
More did you know –

- ... that, in the Rule 90 cellular automaton, any finite pattern eventually fills the whole array of cells with copies of itself?
- ... that, while the criss-cross algorithm visits all eight corners of the Klee–Minty cube when started at a worst corner, it visits only three more corners on average when started at a random corner?
- ...that in senary, all prime numbers other than 2 and 3 end in 1 or a 5?
- ...that, for all prime numbers p, the pth Perrin number is divisible by p?
- ...that it is impossible to trisect a general angle using only a ruler and a compass?
- ...that in a group of 23 people, there is a more than 50% chance that two people share a birthday?
- ...that the 1966 publication disproving Euler's sum of powers conjecture, proposed nearly 200 years earlier, consisted of only two sentences?
Selected article –
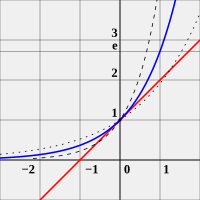 |
| e is the unique number such that the slope of y=ex (blue curve) is exactly 1 when x=0 (illustrated by the red tangent line). For comparison, the curves y=2x (dotted curve) and y=4x (dashed curve) are shown. Image credit: Dick Lyon |
The mathematical constant e is occasionally called Euler's number after the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler, or Napier's constant in honor of the Scottish mathematician John Napier who introduced logarithms. It is one of the most important numbers in mathematics, alongside the additive and multiplicative identities 0 and 1, the imaginary unit i, and π, the circumference to diameter ratio for any circle. It has a number of equivalent definitions. One is given in the caption of the image to the right, and three more are:
- The sum of the infinite series
- where n! is the factorial of n, and 0! is defined to be 1 by convention.
- The global maximizer of the function
- The limit:
-
The number e is also the base of the natural logarithm. Since e is transcendental, and therefore irrational, its value can not be given exactly. The numerical value of e truncated to 20 decimal places is 2.71828 18284 59045 23536. (Full article...)
| View all selected articles |
Subcategories

Algebra | Arithmetic | Analysis | Complex analysis | Applied mathematics | Calculus | Category theory | Chaos theory | Combinatorics | Dynamical systems | Fractals | Game theory | Geometry | Algebraic geometry | Graph theory | Group theory | Linear algebra | Mathematical logic | Model theory | Multi-dimensional geometry | Number theory | Numerical analysis | Optimization | Order theory | Probability and statistics | Set theory | Statistics | Topology | Algebraic topology | Trigonometry | Linear programming
Mathematics | History of mathematics | Mathematicians | Awards | Education | Literature | Notation | Organizations | Theorems | Proofs | Unsolved problems
Topics in mathematics
| General | Foundations | Number theory | Discrete mathematics |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Algebra | Analysis | Geometry and topology | Applied mathematics |
Index of mathematics articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Related portals
WikiProjects
![]() The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
In other Wikimedia projects
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus